Ultrasound of the thorax has been utilised for several decades to investigate suspected respiratory disease in foals and adult horses. In comparison with radiography (especially of adult horses), ultrasound of the thorax can be performed in both an ambulatory and hospital setting. Initial screening can typically be performed with equipment readily available to most equine practitioners, with more advanced, follow up imaging performed using more specialised equipment as required. In horses with suspected intrathoracic disease, ultrasound can be used to identify:
- Pleural effusion
- Pneumothorax
- Rib fractures
- Pulmonary parenchymal disease
- Diaphragmatic hernias
- Other miscellaneous conditions.
Indications
Ultrasonographic examination is indicated in the investigation of suspected respiratory disease in foals and horses. Clinical findings which might prompt ultrasound investigation would include dull lung sounds ventrally (suggestive of pleural effusion), dull lung sounds dorsally (suggestive of pneumothorax) and fever and so called ‘large airway’ sounds (suggestive of pneumonia). In horses and foals with suspected thoracic trauma, ultrasound can be very useful to identify fractured ribs and haemo- or pneumothorax.
Equipment
The initial choice of transducer will depend on the suspected pathology and can be changed as needed depending on the abnormalities subsequently identified. In general, higher frequency transducers will be best for superficial disorders such as pulmonary consolidation and rib fractures, whereas lower frequency transducers will be required to fully evaluate large volume pleural effusion (Table 1).
Table 1. Recommended transducer frequencies based on depth of required image
| Depth required | Transducer frequency (mHz) |
|---|---|
| 5–6 cm | 7–15 |
| 6–10 cm | 6–10 |
| 15–30 cm | 2.5–3.5 |
Method
In foals and most adult horses, clipping is not required, although in horses with a thick, long coat, especially if they are also ‘over conditioned’, clipping will enhance image quality. The coat should be brushed clean of debris, and surgical spirit or ultrasound gel applied to skin or hair. The entire thorax should be imaged, starting (typically) caudally and moving in a cranial direction, with the transducer placed between the ribs and moved in a dorsal to ventral direction. The lung is typically visualised between approximately intercostal space 16 and 4. The cranial mediastinum can be visualised cranial to the heart by pulling the right forelimb forward and placing the transducer in as cranial position as possible, angled forward and towards the left shoulder. Alternatively, the transducer can be placed on the triceps muscle and the mediastinum imaged deep to the musculature and cranial to the heart. The caudoventral area of the neck can be assessed and can be useful in horses with suspected lymphoma as the caudal deep cervical lymph nodes can be visualised (Janvier et al, 2015). The entire pleural surface should be examined by ensuring the dorsal spinous musculature is visualised proximally prior to imaging the lung, and that the diaphragm, abdominal organs and viscera are imaged ventrally. Viewing areas in both inspiration and expiration may enhance visualisation of peripheral lesions which may be variably aerated. Angling cranially and caudally between ribs may also help identify lesions which lie under a rib. In horses where the intercostal spaces are not easily identified, running a finger between the ribs and following this with the transducer can sometimes be helpful to ensure intercostal spaces are not ‘jumped’. Any images obtained should be labelled with the side of the thorax, the intercostal space and a method by which the lesion can be located in a dorso-ventral orientation (typically the point of the shoulder is used as a reference point).
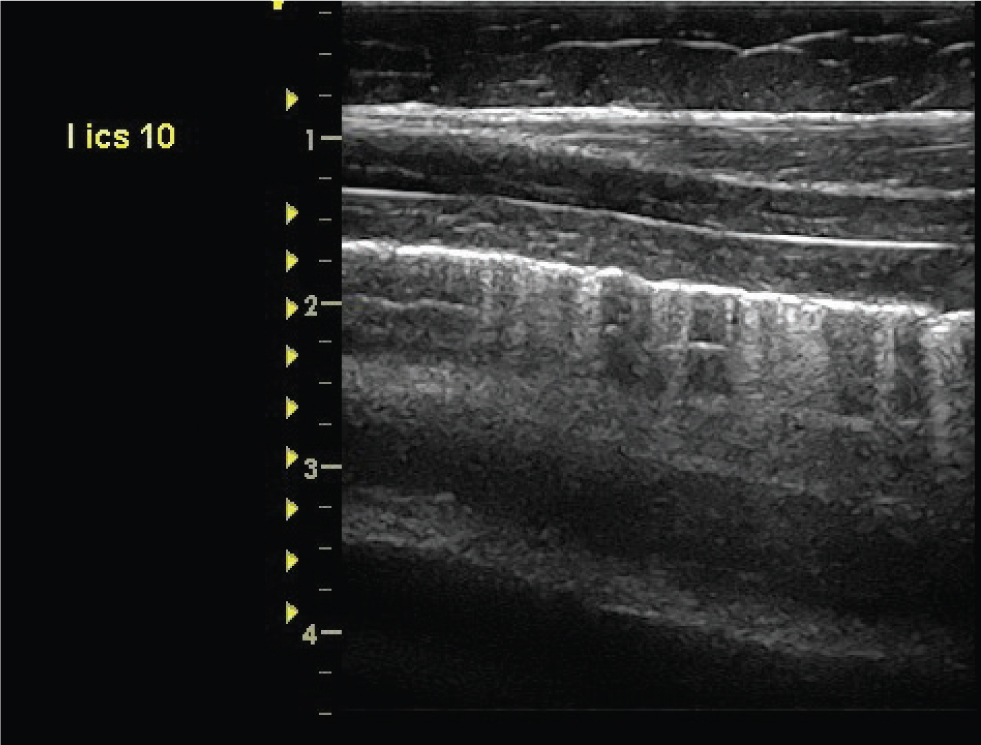
Normal appearance
The normal visceral pleural surface appears as a straight hyperechoic (white) line with characteristic reverberation air artefacts (Figure 1). The ribs can have a similar appearance but can be distinguished from the pleural surface by their more superficial location and the fact that they do not ‘glide’ with respiration. This gliding motion is best appreciated at the most ventral aspect of the intercostal space where the pleural surface moves dorsally with expiration and ventrally with inspiration. Pleural effusion should not be present in normal horses, although on occasions a very small volume (up to several centimetres) can be imaged in the cranial most intercostal spaces. The diaphragm should be seen as a muscular band between the thoracic cavity and the abdominal cavity.
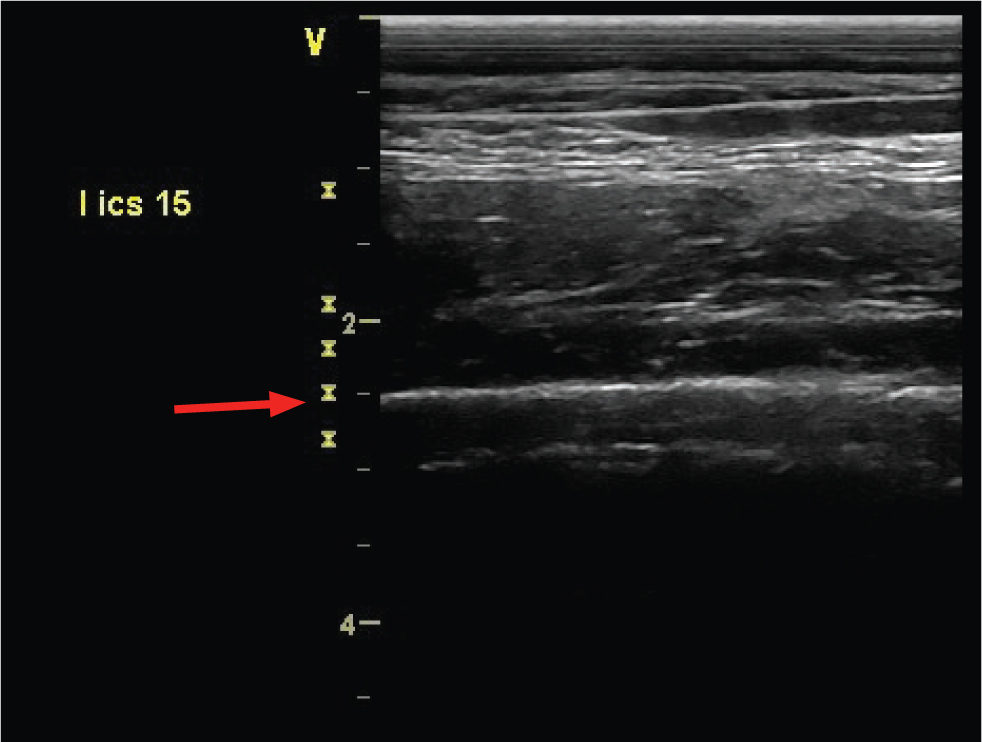
Abnormal findings
‘Comet Tail’ artefacts
Comet tail artefacts are bright white hyperechoic reflections on the pleural surface (Figure 2). They occur due to the presence of a small area of non-aerated lung in the pulmonary periphery. The ultrasound beam penetrates through the area due to the lack of aeration and is then reflected back once normally aerated lung is encountered. The resultant artefact forms a characteristic ‘comettail’. Comet tail artefacts are non-specific findings, and may represent small areas of consolidation, fluid accumulation within the parenchyma (such as pulmonary oedema) or scarring from a previous episode of pulmonary disease. Comet tail artefacts which are diffuse and extend beyond the ventral aspect of the lungs are considered clinically significant.
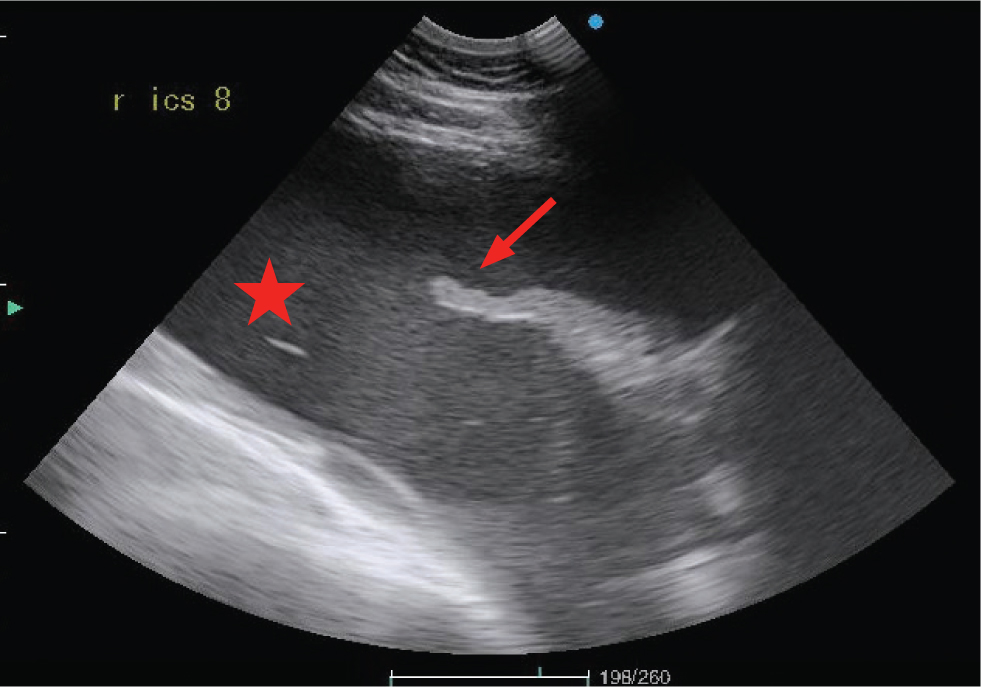
Pleural fluid
Fluid within the pleural cavity is easily visualised with ultrasound. The visceral pleural surface will be separated from the thoracic wall by the fluid and will thus appear deeper than normal. Diseases which can result in accumulation of fluid within the pleural cavity include pleuropneumonia, neoplasia (such as lymphosarcoma or mesothelioma) or trauma. The appearance and amount of fluid should be characterised. Anechoic fluid is likely to have low cellularity and protein concentration (for example, a transudate; Figure 3), whilst an increasing echogenicity is characteristic of highly cellular fluid, such as an exudate (Figure 4). Hyperechoic, swirling pleural fluid is characteristic of haemothorax (Figure 5). The amount of fluid within the pleural cavity can be estimated by determining the height of the imaged fluid. If fluid can be visualised within the dorsal most portions of the pleural cavity, 15–30 L (or more) of fluid (depending on size of the horse) may be present. To aid in the analysis of serial ultrasonographic evaluations, a reference point for measuring the ‘amount’ of pleural fluid is useful. The distance above or below the point of the shoulder at which pleural fluid can first be visualised, at each intercostal space, is commonly used. Because horses typically have a fenestrated, or ‘incomplete’ mediastinum, pleural fluid accumulation is typically bilateral, although inflammatory diseases such as pleuropneumonia may result in occlusion of these fenestrations. In a study examining the cause of pleural effusion in horses residing in the UK (Johns et al, 2016), large volume fluid was more likely to be associated with a diagnosis of neoplasia, compared to smaller volume fluid. In that study, 38% of 69 horses with pleural effusion were diagnosed with neoplasia; horses with neoplastic effusions had a mean of 32.2 L drained from the pleural cavity at admission compared to 9.8 L in horses with a septic effusion.
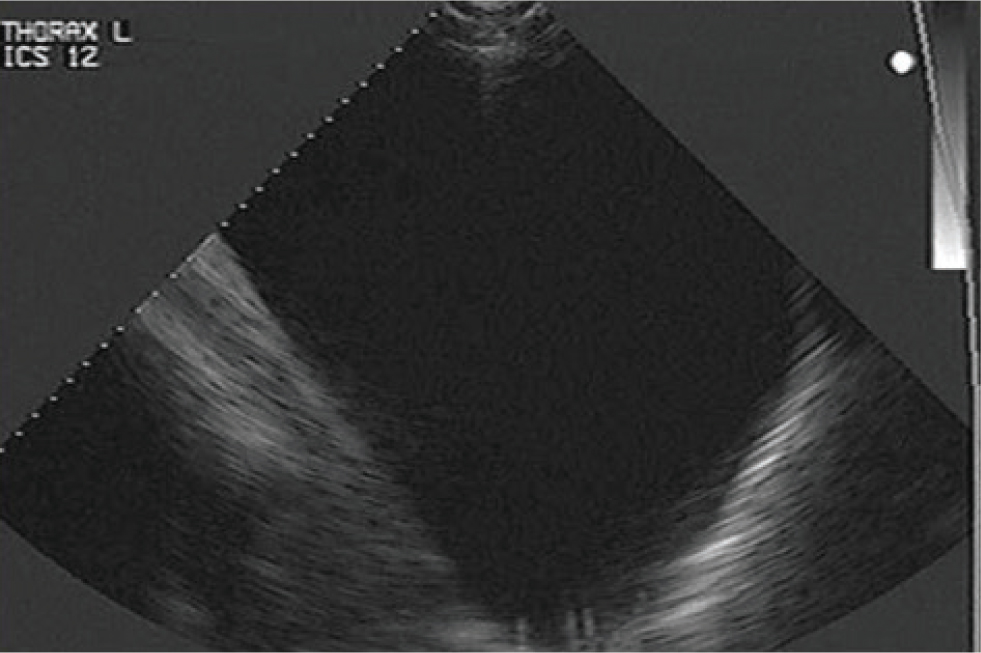
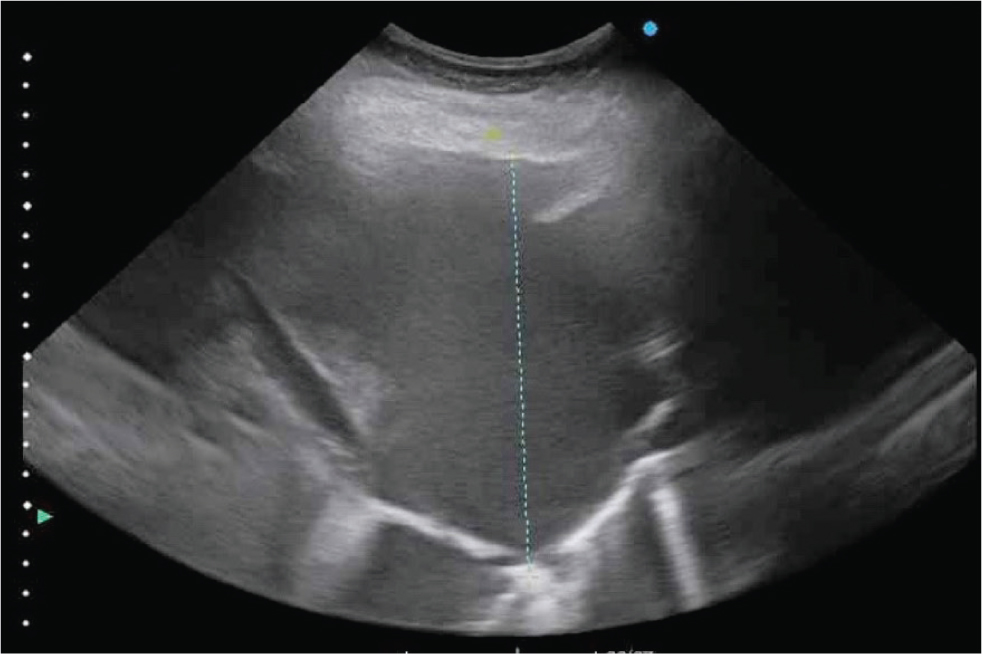
Pneumothorax
Accumulation of air or gas within the pleural cavity can occur as a result of thoracic trauma, anaerobic pleuropneumonia with gas-producing bacteria, a bronchopleural fistula or iatrogenically following thoracic drain placement. Pneumothorax without significant pleural fluid accumulation can be challenging to identify, as the air appears ultrasonographically similar to the normally aerated visceral pleural surface. The ‘gliding lung sign’, which is seen in normally aerated lung as synchronous movement of the pleural line relative to the chest wall during each respiratory cycle, is absent with a pneumothorax. Although radiography has been considered the gold standard for the diagnosis of pneumothorax, a recent study showed ultrasound to be a more sensitive method than radiography for identifying experimentally induced small volume (up to 250 ml) pneumothorax (Partlow et al, 2017).
Fibrin
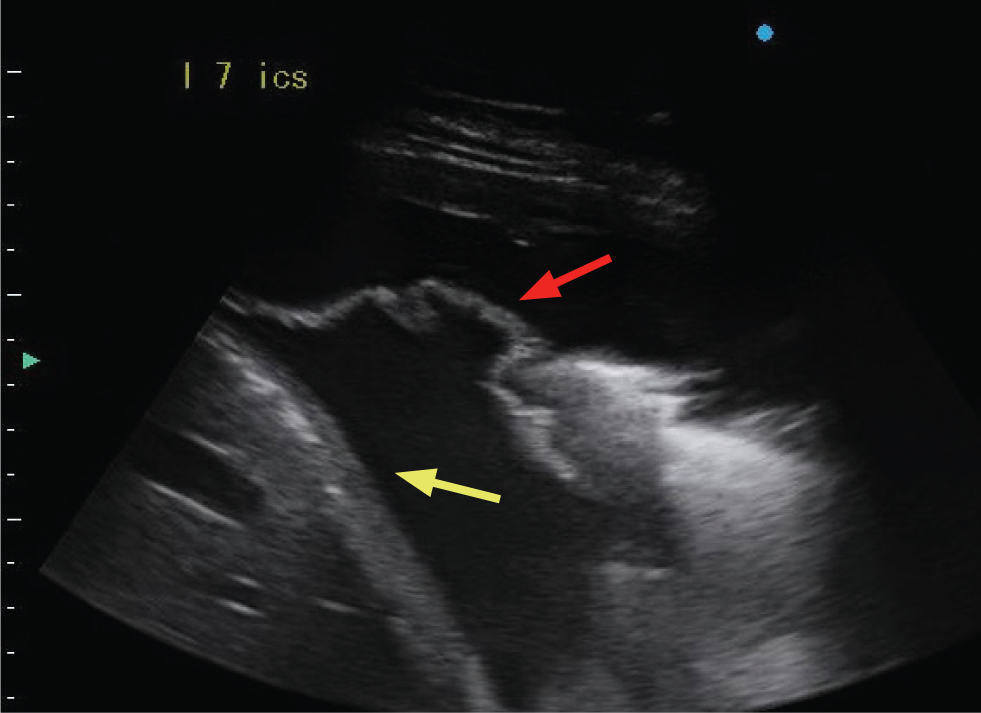
Fibrin accumulation within the pleural cavity is a common sequela of inflammatory pleural diseases such as pleuropneumonia. In one study, 85% of horses hospitalized with pleuropneumonia either had fibrin present at admission or developed fibrin deposition during hospitalisation. The presence of fibrin was associated with a poorer outcome (Tomlinson et al, 2015). Fibrin appears as hypoechoic to hyperechoic strands, or as sheets that line the pleural surfaces. With disease chronicity, fibrin can form adhesions between pleural surfaces and to the diaphragm, which can interfere with the normal gliding movement of the lungs. Fibrin strands can cause loculations within the pleural fluid, resulting in a ‘lace-like’ appearance (Figures 6-9).
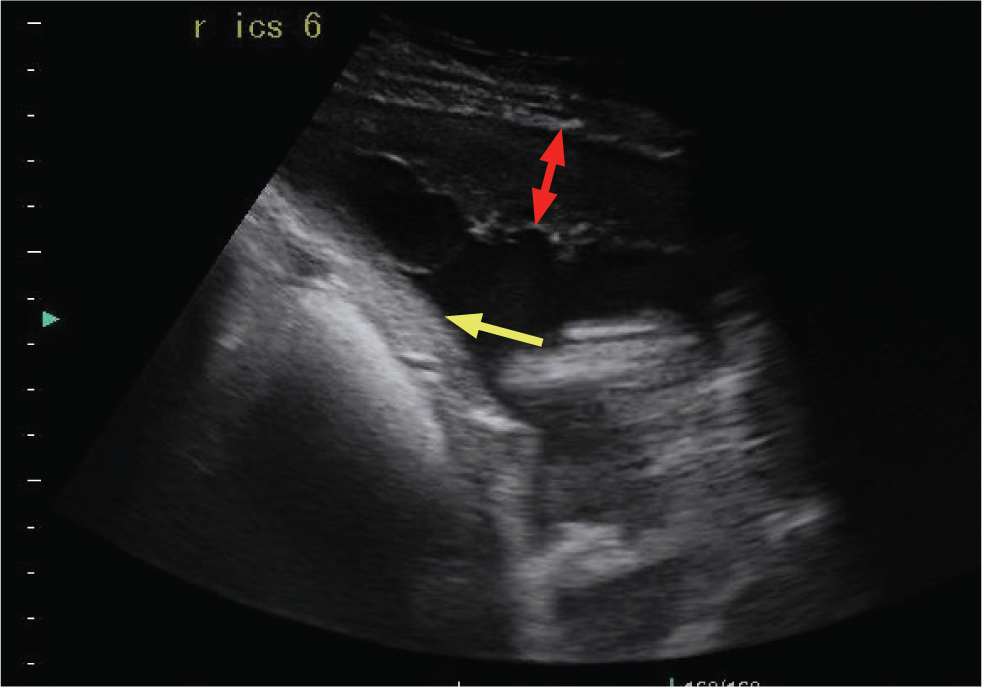

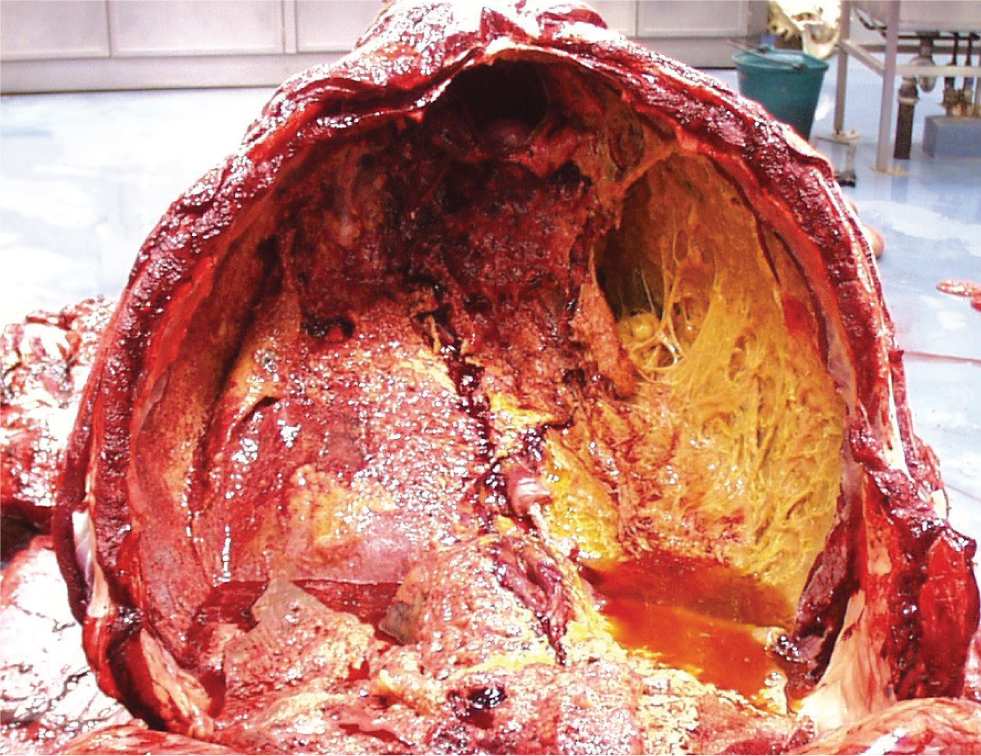
The pericardial diaphragmatic ligament should not be confused with fibrin strands. This is a normal pleural reflection, extending from the pericardium to the diaphragm, becoming ultrasonographically visible when pleural fluid causes it to ‘float’ within the effusion. Typically, it is thicker than fibrin (Figure 10).
Atelectasis
Compression of the pulmonary parenchyma can occur secondary to either pleural effusion or pneumothorax. When secondary to the presence of effusion, the ventral portion of the lung tip appears as a narrow triangular structure in which both bronchi and pulmonary vessels can be imaged. In comparison to consolidated lung, the atelectatic lung tip appears to float within the pleural fluid (Figure 4).
Consolidation
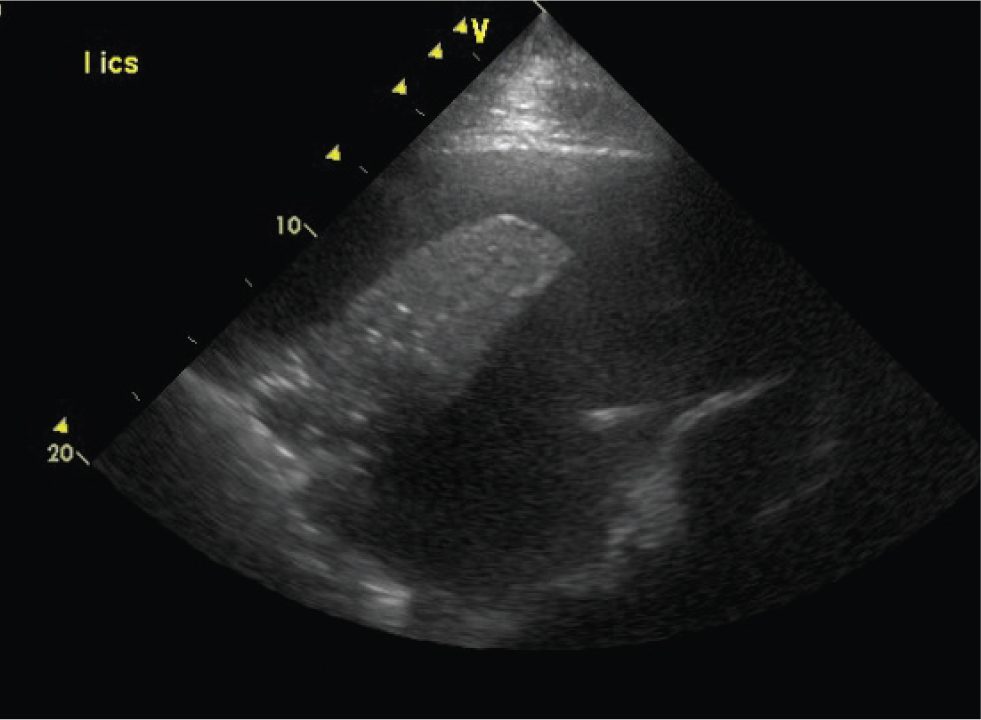
Consolidation of the lung refers to a lack of aeration in the pulmonary parenchyma due to an accumulation of fluid or a cellular infiltrate. Consolidated areas can be imaged as discrete areas throughout the lung, or can involve predominately the ventral lung, depending on the disease process (Figure 11). Ultrasonographically, these areas are characterised by a loss of the characteristic bright white hyperechoic line of the pleural surface, and replacement with a hypoechoic area in the parenchyma. If the ventral lung tip is consolidated, it appears as a triangle or wedge-shaped area. Air bronchograms may be seen if the area of consolidation is extensive. Air bronchograms are seen as hyperechoic free gas echoes within the hypoechoic consolidated lung. An attempt to characterise the extent or size of the consolidated area should be made. In the case of a discrete area of consolidation, measurement of the width and depth of the area can easily be made.
Abscesses and masses
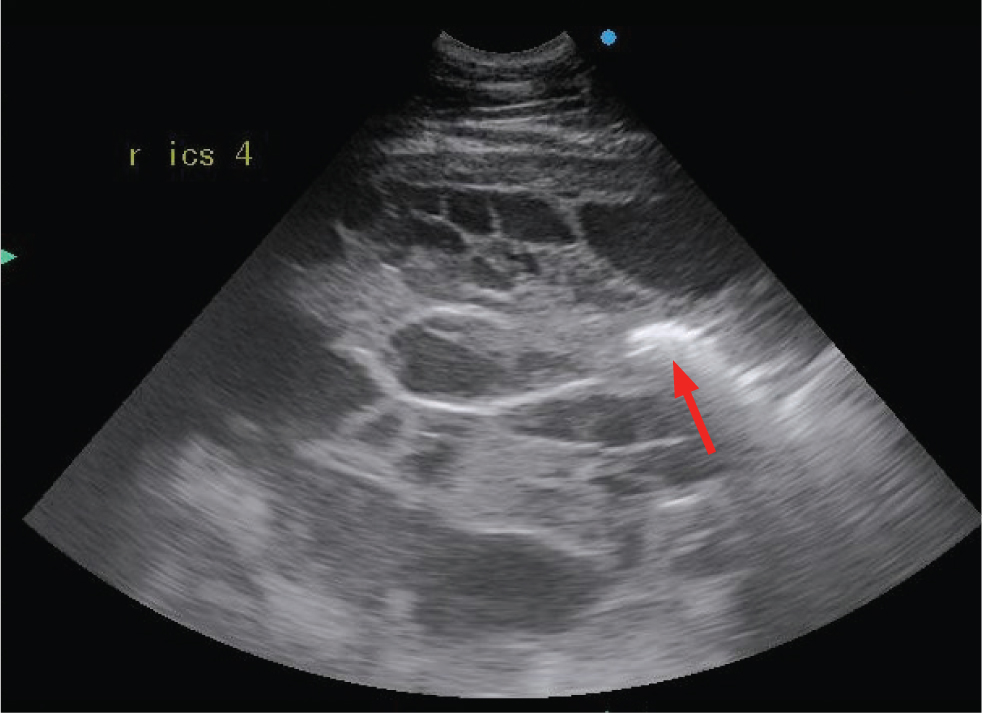
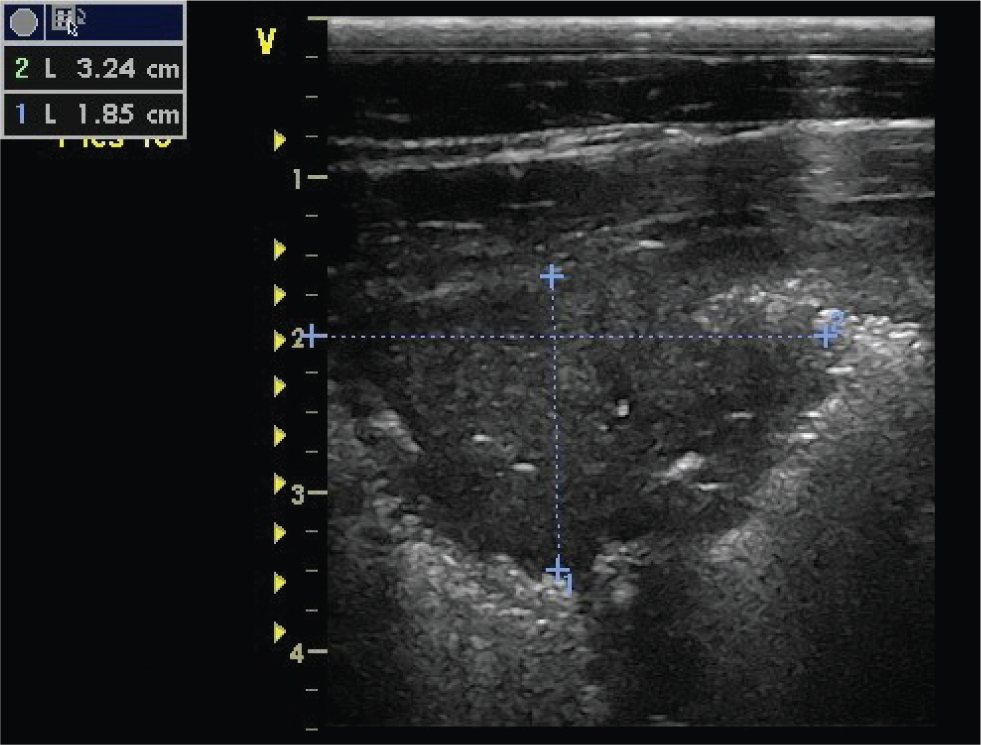
Pulmonary abscesses are most frequently identified in foals with pneumonia caused by Rhodococcus equi or Streptococcus zooepidemicus, although they can also be seen in adult horses with pleuropneumonia or bronchopneumonia. Abscesses appear ultrasonographically similar to consolidation, as a hypoechoic area of lung (Figures 12 and 13). However, abscesses lack normal parenchymal anatomy, and as such, air bronchograms will not be seen within an abscess. An abscess is usually more anechoic than an area of consolidation. Capsules may be seen in abscesses caused by R. equi but are otherwise not commonly identified.
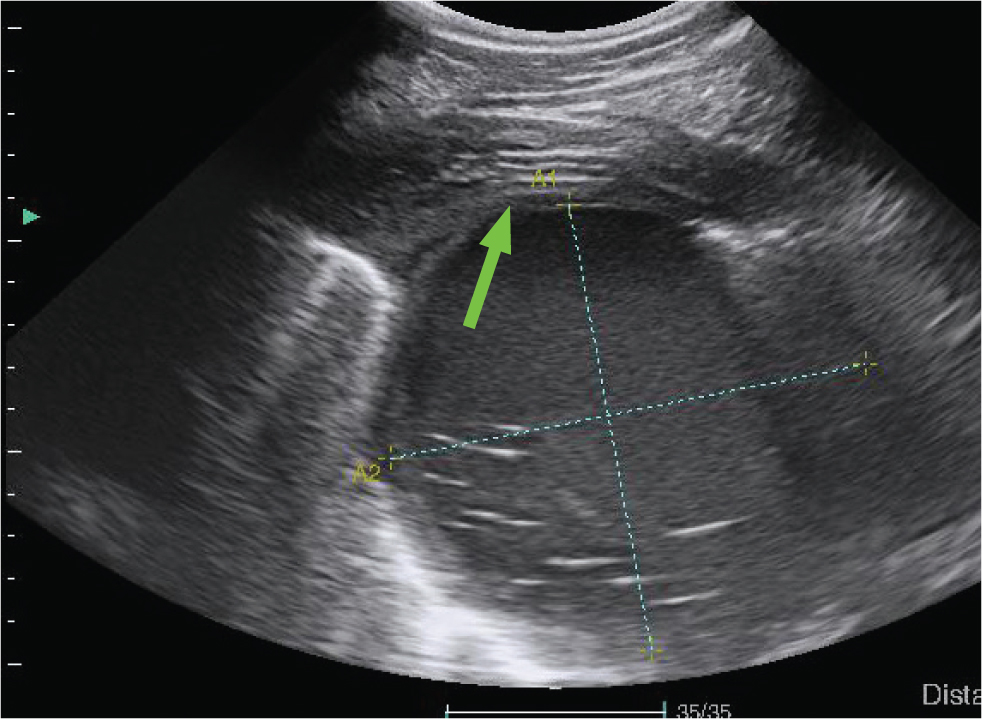
Other masses identified within the pulmonary parenchyma or pleural space may represent neoplasia (primary or metastatic), granulomas, fungal pneumonia or interstitial pneumonia (Figure 14).

Screening foals for pneumonia
Ultrasound has become an integral tool in assessing foals with suspected pneumonia. On farms with endemic R equi pneumonia, ultrasound, in combination with clinical examination and white blood cell count, is used to determine both which foals require treatment and assess response to treatment. A total abscess score is generated by adding together the diameters of individual abscesses (only those ≥1 cm are included). In one study, foals with total abscess scores of between 5–10 cm, mild clinical signs (no dyspnoea) and white blood cell counts less than 21x109/ul were as likely to recover when treated with a placebo, as compared to different antimicrobial regimens (Venner et al, 2013a). In a follow up study, foals with a higher abscess score (8–15 cm) that were treated with antimicrobials were significantly more likely to recover than foals treated with a placebo, emphasizing the utility of ultrasound for monitoring and decision making in foals with pneumonia (Venner et al 2013b).
Rib fractures
Ultrasound can be used to identify rib fractures in adults, and in particular in neonatal foals where fractures may be present without accompanying clinical signs. Fractures are most commonly identified close to the costochondral junction as discontinuities in the hyperechoic bony surface, with or without displacement and fragments, and may be associated with a surrounding haematoma. In one study of foals admitted to an intensive care, 19 out of 29 had rib fractures diagnosed via ultrasound, compared to 5 out of 26 diagnosed radiographically (Jean et al, 2007).
Conclusions
Ultrasonographic examination of the thorax can be easily performed as a screening tool for the presence or absence of pleural effusion or surface abnormalities within the pulmonary parenchyma. Specialised equipment is not required for this initial screening, and if abnormalities are suspected or detected, then further investigation using more specialised equipment can then be performed.
KEY POINTS
- Ultrasound examination of the thorax is a useful tool in the investigation of suspected respiratory disease in foals and adult horses.
- Ultrasound examinations can be performed in both an ambulatory and clinic setting.
- An understanding of the benefits and limitations of the modality is key to obtaining the most useful information from a sonographic examination.
- Sequential examinations can be useful to monitor for improvement or resolution of disease.


